
In developing countries, access to healthcare is often limited by financial constraints. Individuals often have to pay out of their pocket even for very serious diseases that require hospitalization and heavy treatments. This system leads to impoverishment in already poor economies. However, health problems don’t only contribute to impoverishment because of the cost of the treatment. Indeed, the consequences of being sick, such as a decreased ability to work or to take care of the household, are equally costly.
What is more, individuals often give up going to the doctor’s because they know they won’t be able to pay. This can cause premature deaths or the dissemination of contagious diseases.
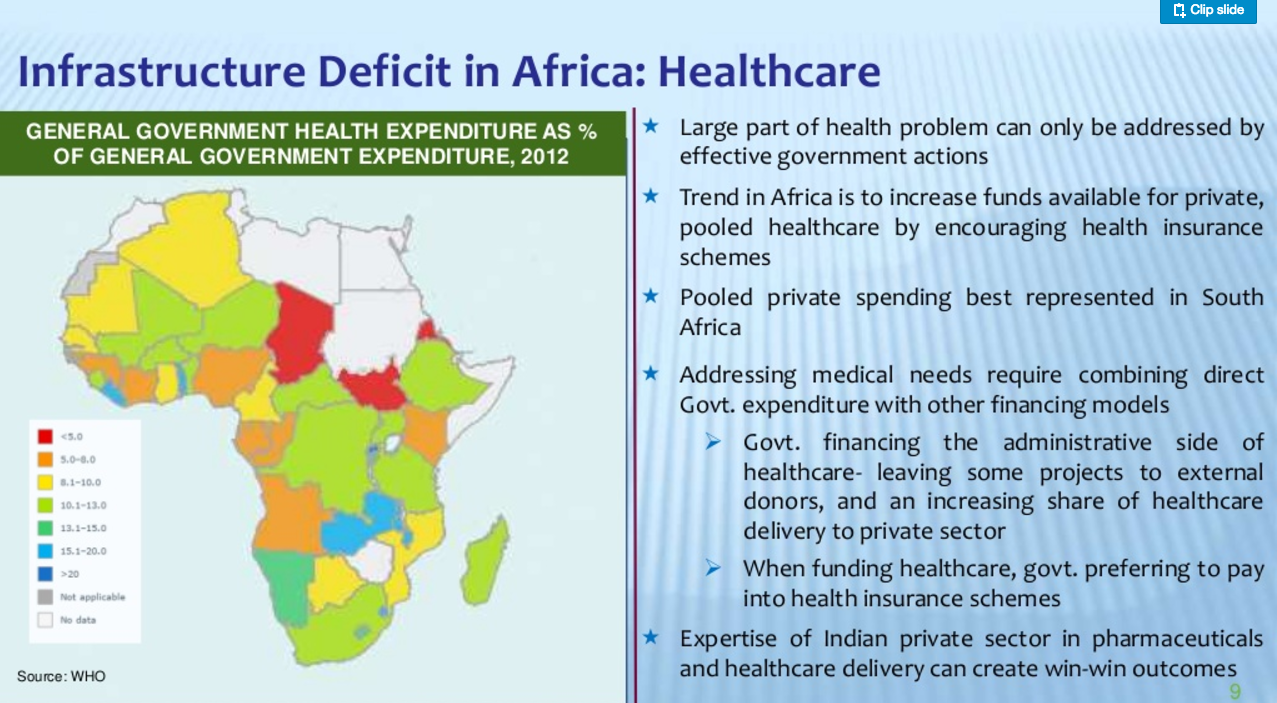
Health is Accountable for 40 percent of Household expenditure
A study of 59 developing countries found that healthcare is accountable for 40% of all household expenditure against only 8.8% in developed countries such as France. This huge gap is mainly due to the fact that individuals in developing countries often don’t have health insurance meaning that they have to pay everything out of their pocket. Developing countries are in the process of building health insurance systems. These systems have 3 main objectives: avoid impoverishment due to high health expenditure, increase the use of health services and last but not least, improve health levels.
Getting To The Unbanked
In developing countries, there is a main problem when it comes to implementing health insurance: the unbanked. Paying for a service with a credit card or a bank transfer has become so current that it is hard to imagine what the world looked like before these financial services arrived. Nevertheless, there are still 2.5 billion people today in the world that are unbanked or underbanked meaning that either they don’t have access to financial services provided by banks or they rarely use them. This means that these people are unable to subscribe to any type of health insurance provided by a private company. Indeed, many of them only accept credit card payments or bank transfers.
Health insurance companies have quickly realized that they are missing out on a whole part of the population by restraining their payment methods. Indeed, in developing countries, most of the individuals use either cash or sometimes pre-paid credit cards. Some companies have therefore adapted to the habits of the emerging markets and now accept pre-paid cards as a form of payment. However, this is still not enough to cover a large part of the population.
Mobile Financial Services Can Leverage Access To Health Insurance
Although many of the people living in developing countries in Asia, Africa, Latin America and the Middle East do not have access to financial services provided by banks, they do have access to mobile phones. Indeed, the market penetration for these products is around 50%.
Mobiles have become a way to reach and interact with the world’s poorest. Therefore, many health companies are creating partnerships with local phone providers. In countries in which people are sometimes forced to walk tens of kilometers before reaching the first hospital, the interest for mobile health services is evident.
When it comes to health insurance, mobile phones could be, once again, of great use. If we start from the observation that the lack of health insurance is partially due to the fact that people are unbanked, we could potentially use the phone as a payment method. For instance, the price of a service can be debited from the mobile phone balance. This method is already being deployed in emerging countries.
Financial Services For The Unbanked
Mobiles phone have a great potential in terms of bringing new services to individuals in emerging countries. Some companies are actually specializing in the market. Humaniq, a blockchain-based app that aims to provide financial services to the unbanked, is one of them. Humaniq allows individuals to simply and rapidly register in the app and send money instantaneously anywhere in the world. When applied to health insurance, this technology has the potential to bring coverage to millions of unbanked people that had no payment method other than cash.
Social and Private Health Insurance Systems
It is important to distinguish two types of health insurance: social health insurance where the government often pays on behalf of the people that can’t afford the costs themselves and private health insurance where individuals are covered upon paying a monthly subscription. The second kind is more difficult to implement in developing countries because low-income individuals are exposed to more risks than people from developed countries. Insurance companies are therefore not always willing to take that risk. Some developing countries have however deployed social health insurance systems over the last decades and are about to extend the coverage to the informal sector. These initiatives have been supported mainly by NGOs but governments are slowly stepping in for a scale-up.
The observation is simple: billions of people do not have access to health insurance. This means that they are forced to pay all the expenses from their pocket. Many of them do not go to hospitals anymore because they cannot afford the costs. With the emergence of new technologies and the democratization of mobiles phones, new models appear to reach these individuals. Whether it is by proving health services or empowering a new kind of payment method, 2.5 billion people are finally given the change to be a part of the global economy.
Thought leadership series on new trends and blockchain, powered by Humaniq.
Launched in 2016, Humaniq aims to provide mobile finance to the 2 billion unbanked population through its mobile app for good, that uses biometric authentication to replace traditional methods of ID and security. Humaniq’s open source stack and API will be available for startups and other businesses to build services on its core technology, making it easy to adapt their service and plug it into Humaniq’s network to reach a huge, untapped audience.

My name is Anca Petre and I am a Pharm. D and Business double degree candidate at Université Paris-Saclay and INSEEC Business School in London and Paris. In my own work, I primarily focus on the crossroads between healthcare and digital technologies. I am currently working on a research about the possible applications of Blockchain in Healthcare and I contribute to Blockchain Age and Intelligent HQ.
I particularly enjoy working the sectors’s startup environment. I have previously worked at e-ssencials, a startup which develops digital solutions for patients with chronic diseases. I have also participated in three hackathons to help develop and further innovate the healthcare circuit.
I worked at Sanofi in the Biotechnologies Department where I successfully managed to reduce the production time by half for several products.
At university, I am the founder and president of the Speak Up ! Association which allows over 500 students to improve their public speaking skills.












