Automated pipetting and liquid handling robotics are crucial elements transforming efficiency and accuracy in today’s laboratories. In 2023, the market for these systems soared to approximately $2.82 billion, driven by a steady annual growth rate exceeding 7.4%. This growth is largely driven by escalating demands in the biopharmaceutical sector for advanced, high-throughput experiments and exacting standards in sample management.
As laboratories strive for increased throughput and reduced errors, automated liquid handling technologies have become indispensable. These systems go beyond mere automation, integrating advanced robotics to manage fluids with unparalleled precision. They cater to diverse applications, from genomic research to drug discovery, where precise and consistent liquid handling is paramount.

Technological Advancements in Robotics
In the past few years, there have been notable developments in robotics, specifically in automated pipetting and liquid handling. Companies have introduced systems featuring cutting-edge robotic technology that provide improved precision and faster operation than previous models.
These improvements are a direct response to the increased need for higher production rates and exact handling of liquids. Current models are capable of dealing with everything from small amounts of sensitive organic compounds to thick liquids, all while reducing the inconsistencies often seen with manual processes.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning into robotics used for liquid handling represents a significant change in how laboratories are automated. These advanced systems continuously learn from their tasks, adjusting their operations in real time to prevent mistakes and make lab work more efficient.
AI algorithms also anticipate when maintenance is required, minimizing downtime and prolonging the equipment’s lifespan. This predictive ability guarantees that the robotics perform at their best, delivering reliable results essential for delicate experiments.
Moreover, by harnessing AI and machine learning, these robotics enhance the precision and consistency of experimental outcomes. They adapt dynamically to varying conditions, ensuring optimal performance across a range of scientific tasks. This integration exemplifies how advanced technology can revolutionize laboratory workflows, paving the way for more efficient research and development processes.
Enhancements in User Interface and Usability
Improvements in how users interact with and use automated pipetting systems have made these technologies easier for lab staff to adopt. Today’s liquid handling robotics feature user-friendly touchscreens and graphical interfaces that simplify programming and operation.
These interfaces enable technicians with limited technical expertise to effectively manage complex systems, expanding the practical application of advanced robotics in numerous labs. Such advancements ensure that even labs with less specialized personnel can benefit from the precision and efficiency offered by modern robotic technology, transforming how experiments are conducted across scientific disciplines.
Customization and Flexibility
A key highlight of the latest liquid handling robotics is their ability to be tailored and their versatility. Modern systems are designed to support a wide variety of laboratory demands, adjusting seamlessly to different operational procedures.
Whether performing basic dilution operations or managing several elements for intricate biochemical tests, these robots can be set up to align with the distinct needs of any lab environment. This adaptability not only boosts lab efficiency but also guarantees that the systems remain relevant and useful as research demands change.
Impact on Research Efficiency
The impact of automated pipetting and liquid handling robotics on research productivity is profound. These technologies greatly decrease the time dedicated to monotonous tasks, lower the chances of mistakes caused by humans, and uphold stringent accuracy levels.
Consequently, scientists are able to tackle larger projects more quickly. The exactness provided by automation ensures experiments can be duplicated more reliably, which is crucial for scientific research.
Environmental and Safety Improvements
Automated pipetting systems play a crucial role in making laboratories more sustainable and safer. These systems reduce waste and use fewer chemicals by handling liquids with precision.
This efficiency not only saves money but also reduces the environmental harm caused by disposing of chemicals. Furthermore, by automating the handling of dangerous chemicals, these systems help keep lab workers safe from potential exposure, improving overall workplace safety.
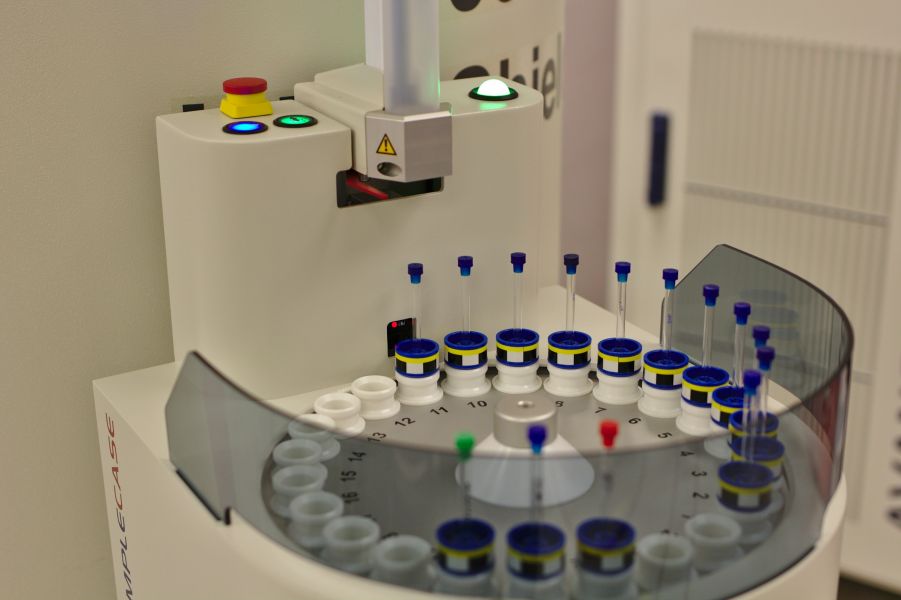
Final Thoughts and Looking Ahead
Recent progress in automated pipetting and liquid handling robotics has consistently raised the bar for laboratory performance. The combination of advanced robotics, artificial intelligence, and a focus on the user experience has led to systems that are not just faster but also more flexible and easier to use.
With the ongoing development of these technologies, we expect to see even more groundbreaking changes that will expand the limits of research and development. The outlook for lab automation is optimistic, with continued improvements set to transform the field and make advanced experiments more widely available to researchers globally.

Founder Dinis Guarda
IntelligentHQ Your New Business Network.
IntelligentHQ is a Business network and an expert source for finance, capital markets and intelligence for thousands of global business professionals, startups, and companies.
We exist at the point of intersection between technology, social media, finance and innovation.
IntelligentHQ leverages innovation and scale of social digital technology, analytics, news, and distribution to create an unparalleled, full digital medium and social business networks spectrum.
IntelligentHQ is working hard, to become a trusted, and indispensable source of business news and analytics, within financial services and its associated supply chains and ecosystems