“Men come together in cities in order to live:
they remain together in order to live the good life.”
— Aristotle
“What is the city but the people?”
— William Shakespeare
“Urbanization, one of humankind’s most successful and ambitious programs, is the triumph of the unnatural over the natural, the grid over the organic… Underway on a scale never before witnessed, one side effect of urbanization is the liberation of vast depopulated territories for the efficient production of ‘nature’.”
— Bruce M
“A smart city is an intelligent town that provides enormous possibilities for human growth through art, culture, social, architectural, economic, political, environmental, and scientific flowering with the optimal mix of nature, technology, humanity, and arts.”
― Amit Ray, Peace Bliss Beauty and Truth: Living with Positivity
Cities are all about people’s lives. Big social groups of people living and collaborating together. Whether you are in London, New York, Singapore, Tokyo or Beijing, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Barcelona these cities offer the best in the world and are able to serve so many millions of people together because of their adoption of smart technologies which makes them leading smart cities.
Smart Cities are the heart of the beating of the best in the world and in the interstice of all challenges, innovation and concerns. Particularly when it comes to organisation of society, citizens, innovation, technology and data, smart cities are the center of all operations and challenges and opportunities.
Smart cities, like the city states in the past embed the highest hopes of humany through the promise of harnessing the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) innovative technologies to improve lives and bring social harmony. However, smart cities represent also and could incarnate the challenges, fears of a dystopian ecosystem of over ‘controlled lives’, making society unfold in some kind of panopticon system, governed by the emergence and disruption coming out of artificial intelligence, IoT, Blockchain and automated devices coming from the augmented tools and software inherent to digital transformation systems.
As big data and Social media flourishes in this environment, revolutionizing the way leaders and citizens interact with space, cities will be the biggest challenge and opportunity for the next 100 years. The data driven technologies that drive the smarter city must be rightly managed and secure, to safely fuel unhindered progress.
As national governments increasingly focus on national issues, cities are at the forefront of all human activities and must take greater advantage of the most advanced technologies to update service delivery. New possibilities and business models target the creation of radical new efficiencies, sustainable solutions for long-standing challenges.
Cognitive computing, blockchain technology solutions and artificial intelligence in particular and its capacity for building citizen engagement, identity and sustainable models of circular economic values, introduces fresh opportunities for government organizations to improve citizens’ lives and the business environment, deliver personalized experiences, and optimize program and service outcomes.
The choices we need to make today are multiple and mostly about what makes a smart city empower our lives and make them matter for multiple reasons. The challenging momentum of technological innovation will continue, and in the next decades will be bigger than in all history of humanity. So the way we plan, manage and architect smart cities has to be done in a way to increase in the near future, giving us new ways to address pending global challenges, in areas such as social inclusion, climate change, inequalities, health or education.
On the other hand, the majority of the human race leaves in societies and these individuals whose lives will depend on such choices will be city dwellers. Yet, for city leaders, investors, and citizens, such choices often remain difficult to make because they are complex, and often rely on imperfect or asymmetrical information. Real estate tactics have often prevailed over transport, energy or waste management concerns. Quality of life seldom received priority over urbanistic, architectural or technological ambitions. And efficiency sometimes eclipses social harmony.
In all avenues of human challenging life, it remains extremely difficult to improve without thinking inclusively and empowering both humans, nature and find a fine tuned balance that can be in some kind of way, measured. It is hence no surprise that so many ‘smart city indices’ have blossomed over the past few years. The main reason is simple: the quasi-totality of existing indices remains technology-centric. But lots of work needs to be done to build the right basis of smart cities balance solutions.
There are a lot of examples of the ways smart cities are creating new jobs and solutions and much more is happening. The city of Barcelona for example is a prime example where the implementation of smart city IoT systems created an estimated 47,000 jobs, saved €42.5 million on water, and generated an extra €36.5 million a year through smart parking alone. We can easily see that many other cities in the world can benefit tremendously from the technological advances that utilize 4IR technologies, AI-blockchain powered IoT solutions. These technological solutions are now helping connect cities, societies, creating new efficiencies and manage multiple infrastructure, and public services.
Building smart cities is the critical job for countries, societies and it is not a one-day business. This should be the main focus of nations and cities governments and it is a collective work that requires a lot of work between different players. It the work of one person or organization but the work of an entire society all tribes that make cities.
Smart cities require planning and special strategy and efforts from all areas of society and economy. Smart cities requires the collaboration of many strategic partners, leaders, and special citizens and their government.
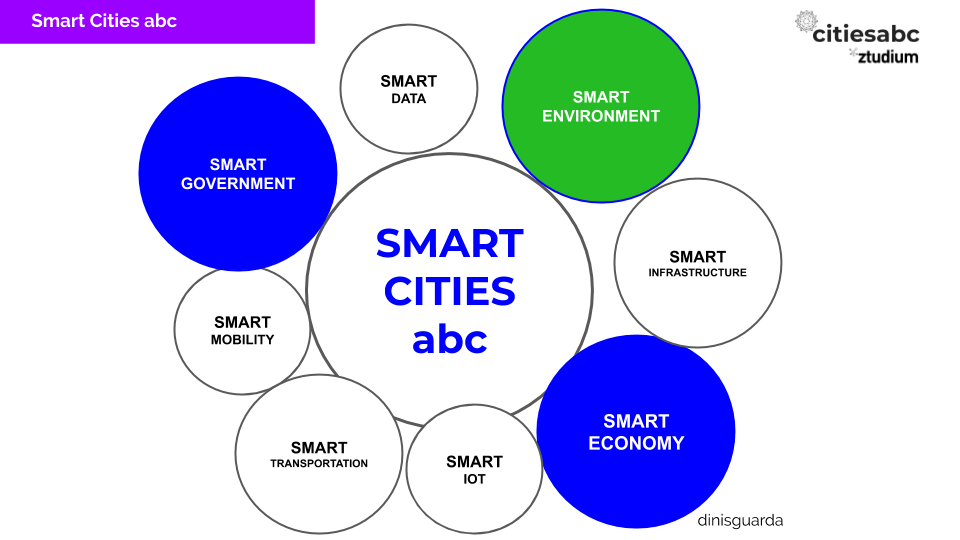
- A strategy and social economic and legal frame from government approved by citizens.
- A collaboration between all players: lawmakers, government organisations, universities, schools, companies and businesses, all citizens major groups represented.
- Align a strategy and goals on how to achieve clear results based on clear budgeting, using reward systems, digital assets solutions, environmental focus systems and capacities to deliver on ambition and needs.
- A set of aligned data and technology infrastructure alignment combining supply chain and identity with blockchain technology and IOT sensors to aggregate systems and data that will managed and expanded by AI tech.
- Create solutions within the requirements and needs of the city and geographical and development stages.
- A network of smart technology things (sensors, cameras, actuators, and so on) for gathering data and managing it.
- Field (cloud computing) gateways that can gather the data from low power IoT devices, store it, and forward it securely to the cloud.
- Streaming data processors for aggregating numerous data streams and distributing them to a data lake and control applications and integrating with AI machine learning systems.
- A data lake for storing all the raw data, even the ones that seem of no value yet and data management systems to understand optimisations and solutions.
- A data warehouse that can clean and structure the collected data and integrate with AI Machine learning.
- Tools for analyzing and visualizing the data collected by sensors
- AI algorithms and techniques for automating city services based on long-term data analysis and finding ways to improve the performance of control applications
- User applications for connecting smart things and citizens
Besides this, there will be issues regarding clear set up on data and identity, security and privacy, and the choice of the right service providers will have to ensure that these smart technologies, devices and services do not pose any threat to citizens’ wellbeing. The solutions should be aligned with a strategy that is people first and focusing on creating services themselves that should be easy to use and employ, so that citizens can adopt them and create empowering development.

Dinis Guarda is an author, academic, influencer, serial entrepreneur, and leader in 4IR, AI, Fintech, digital transformation, and Blockchain. Dinis has created various companies such as Ztudium tech platform; founder of global digital platform directory openbusinesscouncil.org; digital transformation platform to empower, guide and index cities citiesabc.com and fashion technology platform fashionabc.org. He is also the publisher of intelligenthq.com, hedgethink.com and tradersdna.com. He has been working with the likes of UN / UNITAR, UNESCO, European Space Agency, Davos WEF, Philips, Saxo Bank, Mastercard, Barclays, and governments all over the world.
With over two decades of experience in international business, C-level positions, and digital transformation, Dinis has worked with new tech, cryptocurrencies, driven ICOs, regulation, compliance, and legal international processes, and has created a bank, and been involved in the inception of some of the top 100 digital currencies.
He creates and helps build ventures focused on global growth, 360 digital strategies, sustainable innovation, Blockchain, Fintech, AI and new emerging business models such as ICOs / tokenomics.
Dinis is the founder/CEO of ztudium that manages blocksdna / lifesdna. These products and platforms offer multiple AI P2P, fintech, blockchain, search engine and PaaS solutions in consumer wellness healthcare and life style with a global team of experts and universities.
He is the founder of coinsdna a new swiss regulated, Swiss based, institutional grade token and cryptocurrencies blockchain exchange. He is founder of DragonBloc a blockchain, AI, Fintech fund and co-founder of Freedomee project.
Dinis is the author of various books. He has published different books such “4IR AI Blockchain Fintech IoT Reinventing a Nation”, “How Businesses and Governments can Prosper with Fintech, Blockchain and AI?”, also the bigger case study and book (400 pages) “Blockchain, AI and Crypto Economics – The Next Tsunami?” last the “Tokenomics and ICOs – How to be good at the new digital world of finance / Crypto” was launched in 2018.
Some of the companies Dinis created or has been involved have reached over 1 USD billions in valuation. Dinis has advised and was responsible for some top financial organisations, 100 cryptocurrencies worldwide and Fortune 500 companies.
Dinis is involved as a strategist, board member and advisor with the payments, lifestyle, blockchain reward community app Glance technologies, for whom he built the blockchain messaging / payment / loyalty software Blockimpact, the seminal Hyperloop Transportations project, Kora, and blockchain cybersecurity Privus.
He is listed in various global fintech, blockchain, AI, social media industry top lists as an influencer in position top 10/20 within 100 rankings: such as Top People In Blockchain | Cointelegraph https://top.cointelegraph.com/ and https://cryptoweekly.co/100/ .
Between 2014 and 2015 he was involved in creating a fabbanking.com a digital bank between Asia and Africa as Chief Commercial Officer and Marketing Officer responsible for all legal, tech and business development. Between 2009 and 2010 he was the founder of one of the world first fintech, social trading platforms tradingfloor.com for Saxo Bank.
He is a shareholder of the fintech social money transfer app Moneymailme and math edutech gamification children’s app Gozoa.
He has been a lecturer at Copenhagen Business School, Groupe INSEEC/Monaco University and other leading world universities.

























